Important Labor Market Trends: Slowing US Labor Market
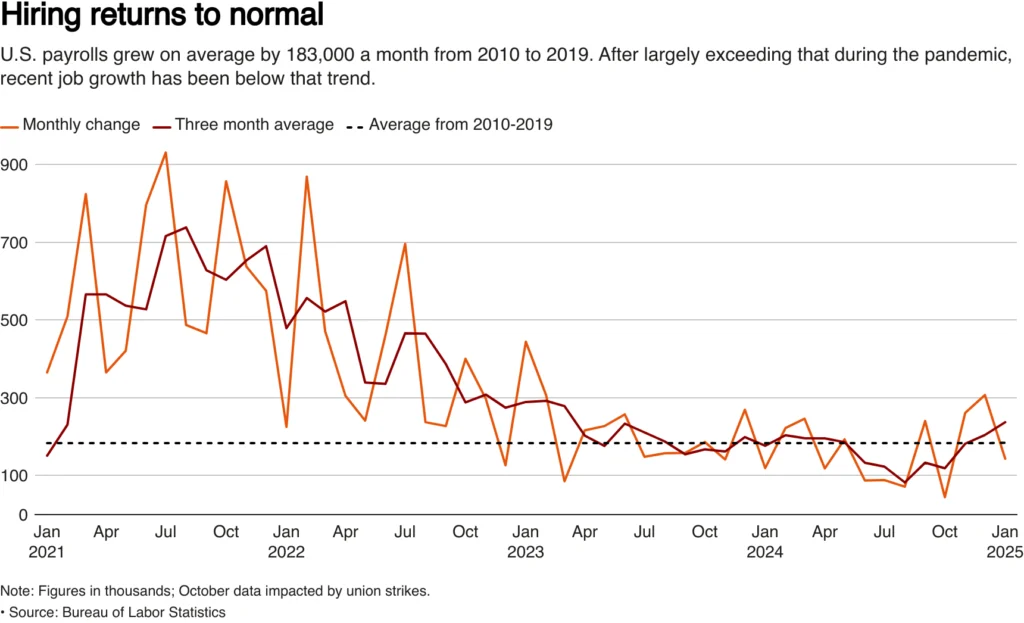
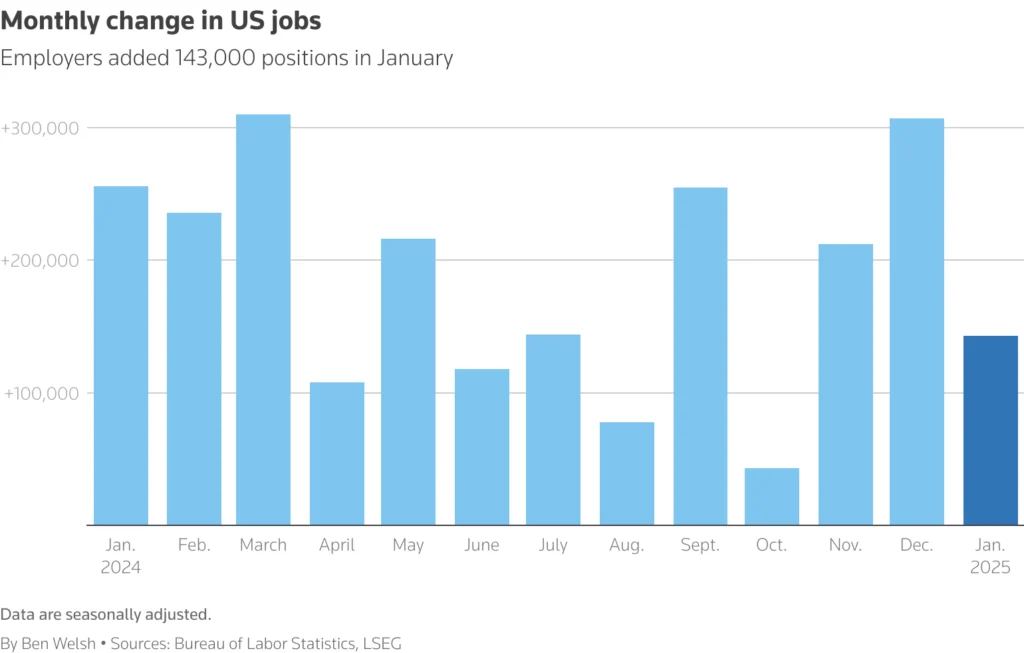
A downturn in the US labor market in January suggested that the momentum behind job creation may be slowing down. Nonfarm payrolls grew by 143,000 jobs, less than 170,000 gains experts had projected. Even though job growth was slowing, the employment rate stayed stable at 4.0% indicating a healthy labor market.
Wages in the US Labor Market and Economic Implications
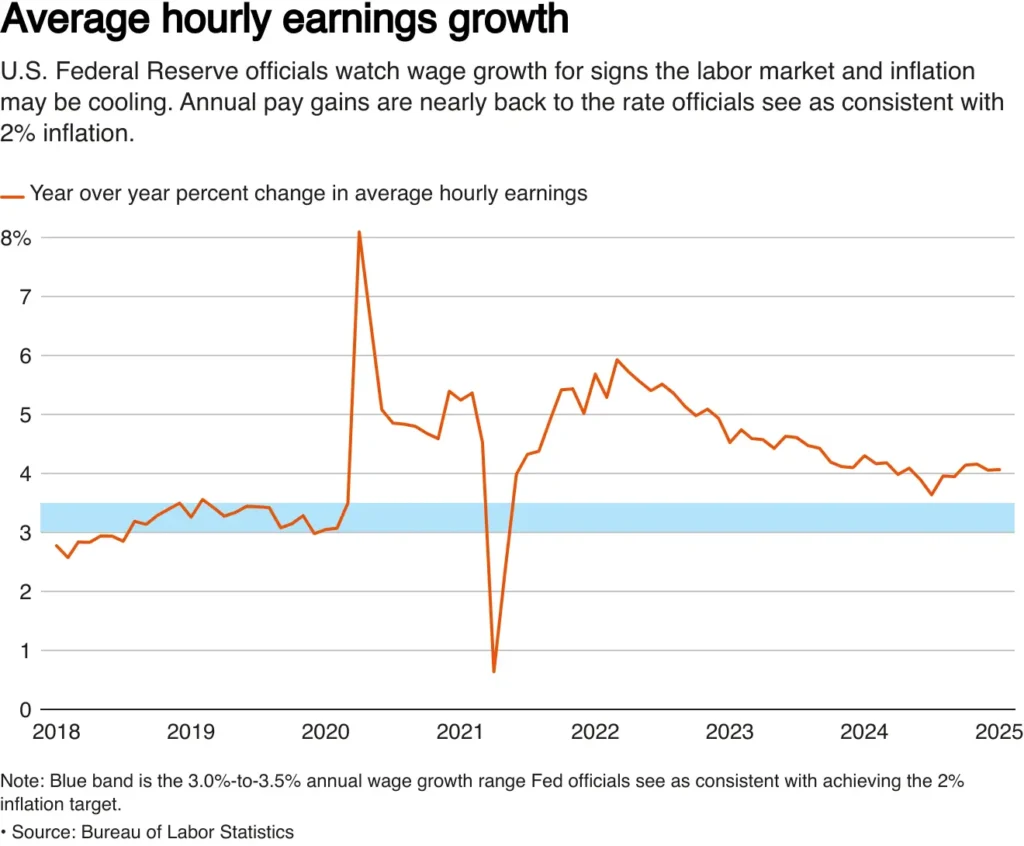
One bright spot for the labour market in January was wage increases. The biggest monthly gain in five months was a 0.5% increase in average hourly wages. The stability of annual wage growth at 4.1% demonstrated the strength of the American labour market. Even as more general economic uncertainty loom, this strong wage growth encourages ongoing consumer spending, which is a vital economic driver.
Sector-Specific Perspectives: Strength and Weakness in the U.S. Labor Market
The healthcare sector emerged as the top contributor to employment gains, adding 44,000 new positions. Other notable contributors included:
- Retail Sector: Added 34,000 jobs, with growth concentrated in general merchandise stores.
- Government Employment: Increased by 32,000 positions, boosting public sector stability.
- Social Assistance Services: Contributed 22,000 new jobs, reflecting demand for community support services.
Conversely, the construction, manufacturing, and professional services sectors reported minimal changes, underscoring a mixed performance across industries.
Implications for the Federal Result: U.S. Labor Market Data
Strong wage growth and a stable unemployment rate highlight the Fed’s cautious monetary policy stance. The central bank is anticipated to hold onto its benchmark interest rate, which is now between 4.25% and 4.50%, until at least June. These numbers support the Fed’s position of making gradual policy changes as it negotiates changing economic circumstances.
Future Challenges for the U.S. Labor Market
In the future, policy uncertainty may present difficulties for the labor market. The trump administration’s proposed immigration restrictions and tariffs may alter industry-specific employment and worker dynamics. Additionally, earlier labor market optimism was clouded by revisions to previous job creation figures that showed 589,000 less jobs were added during the previous year than first projected.
Although the US labor market is still strong, there are still worries about the country’s reliance on lower wage sectors for employment development instead of more established high growth sectors like manufacturing and technology. Resolving these structural and policy related issues is essential to maintaining economic momentum.